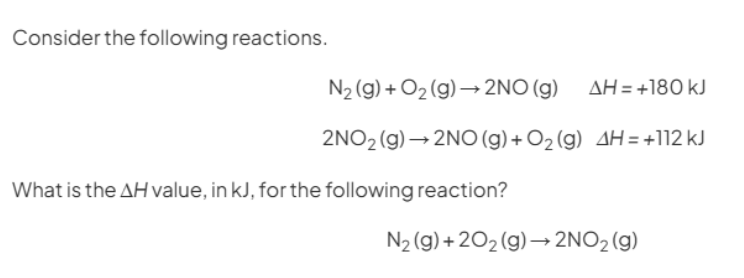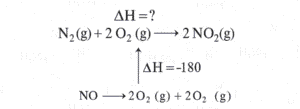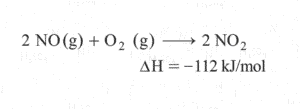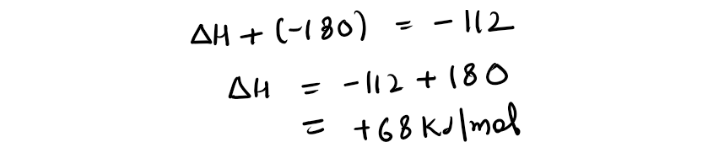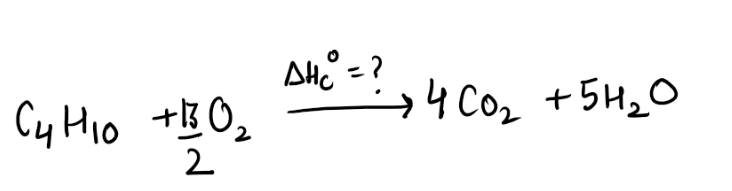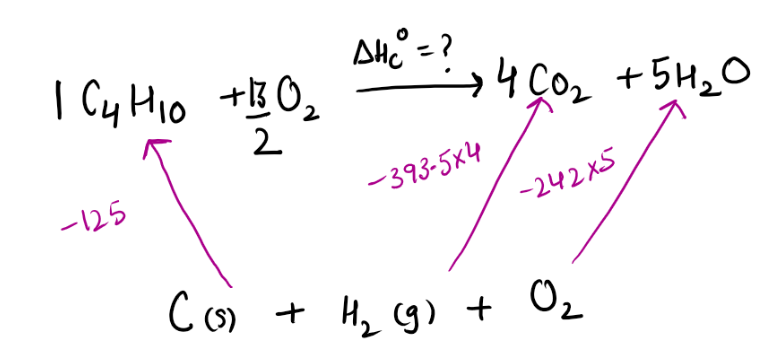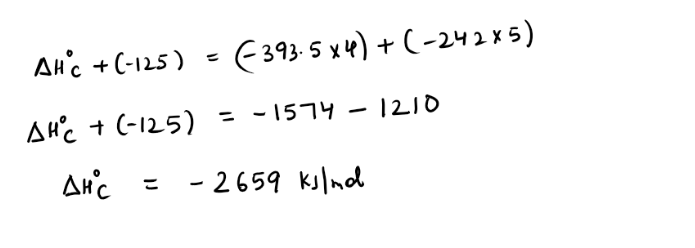Introduction
In chemistry, one of the most elegant principles that helps us to calculate enthalpy change of a chemical reaction. Unlike temperature , mass and other variables which can be calculated using some instrument , Enthalpy cannot be calculated directly.
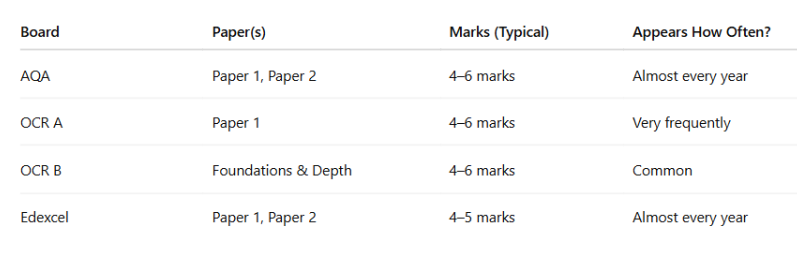
Weightage of Hess Cycle in A levels
FOR AQA
Hess cycle appears in paper1 and paper2
It Usually has 4–6 marks per question involving Hess Cycles.
It almost comes every year but often combined with enthalpy of formation or bond enthalpies
What is Hess’s Law?
Hess’s Law states:
“The enthalpy change of a reaction is independent of the pathway followed to reach the final state(products)
This means that the total enthalpy change (ΔH) of a reaction remains the same, whether the reaction happens in a single step or multiple steps.
The reason this works is because enthalpy is a state function. State functions depend only on the initial and final conditions, not the process used to get there.
Historical Background of Hess’s Law
Hess’s Law was formulated in 1840 by Germain Henri Hess, a Swiss-born Russian chemist.
- At the time, thermodynamics was still developing.
- Hess conducted experiments on heat changes during chemical reactions and observed that the heat evolved or absorbed depended only on the initial and final substances, not on the path taken.
- This discovery laid the foundation for what we now call thermochemistry.
Later, this principle was supported by the First Law of Thermodynamics: energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed.
Hess Cycle is divided into three stages according to marking scheme
- Drawing correct cycles
- Labeling enthalpies correctly
- Applying Hess’s Law formula:
Before stepwise learning Hess Cycle we need to learn few definations of various enthalpy changes
A)Standard Enthalpy of Reactions – The standard enthalpy change when the reactants in the stoichiometric equation react to form the products under standard conditions
B)Standard Enthalpy of Formation – The standard enthalpy change for the formation of one mole of a compound from its elements in their most stable states.
C)Standard enthalpy of combustion – It is defined as the enthalpy change when 1 mole of a substance , undergoes complete combustion and all the reactants and products being in their standard states at the specified temperature.
D)Standard enthalpy change of neutralisation -The enthalpy change when one mole of water is formed by reacting an acid and an alkali under standard conditions
Standard Conditions mean:
- Temperature: 298 K (25 °C)
- Pressure: 100 kPa (1 atm)
- Solutions: 1.0 mol dm⁻³
- All substances in their standard states
Theoretical Representation of Hess’s Law
Imagine three chemical species: A, B, and C.
- If A → C directly gives ΔH₁
- And A → B → C gives ΔH₂ + ΔH₃
Then:
ΔH1=ΔH2+ΔH3ΔH₁ = ΔH₂ + ΔH₃ΔH1=ΔH2+ΔH3
This is the simplest way to see Hess’s Law in action.
Lets try to solve hess cycle in steps –
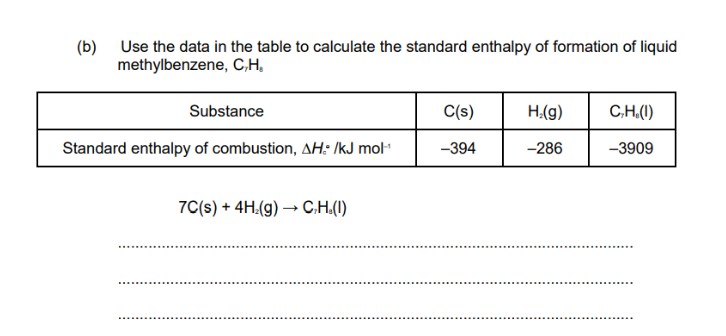
STEP 1) Write the equation for which they are asking for the enthalpy change in a horizontal fashion
Here in this question they are asking to find enthalpy change of reaction for the formation of nitrogen dioxide. Lets write this equation in horizontal manner
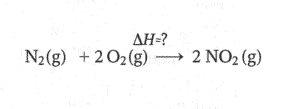 Now we will be using the equations for which enthalpy change are given to us. We will try to generate products and reactants using these equations for the main equation
Now we will be using the equations for which enthalpy change are given to us. We will try to generate products and reactants using these equations for the main equation
STEP2) Using first Equation We can generate nitrogen and oxygen gas. So lets reverse the first equation(Remember if we are reversing the reaction the sign of enthalpy will change)(forgot to put (g) for NO)
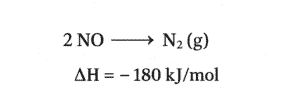
Now arranging this equation in the original equation and constructing hess cycle for it(forgot to put 2 in front of NO)
STEP3)Now using the other equation, If you look closely it is making nitrogen monoxide and oxygen gas from nitrogen dioxide (which is our product of main equation)
Now lets complete our cycle by arranging this equation
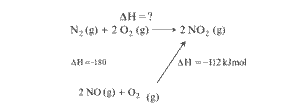 STEP4) We need to follow the direction of arrow heads adding the one with same direction and subtracting from the opposite
STEP4) We need to follow the direction of arrow heads adding the one with same direction and subtracting from the opposite
Mathematical Rules of Hess’s Law
When manipulating chemical equations for Hess’s Law calculations, keep these rules in mind:
- Reversing a reaction → change the sign of ΔH.
- Multiplying a reaction → multiply ΔH by the same factor.
- Adding reactions → add ΔH values.
- Canceling species → ensure intermediate substances cancel properly.
Lets try a previous year question now.
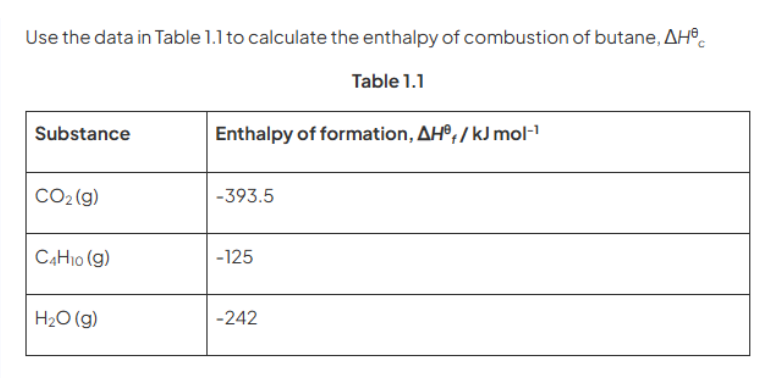
Step1) They are asking to find enthalpy of combustion of butane , So lets write the equation representing enthalpy of combustion of butane(Tip – you must be aware of definition of standard enthalpy of combustion)
Step2) We will be using enthalpy of formation of various molecules (Tip – You must be well aware of definition of enthalpy of formation)
Remember to multiply them using the coefficients that are present in actual equation
For example 4 moles of carbon dioxide are being produced therefore enthalpy of formation needs to be multiplied by 4
Step3) Now we just need to add arrow heads pointing in same direction and subtracting it from one with different arrow head
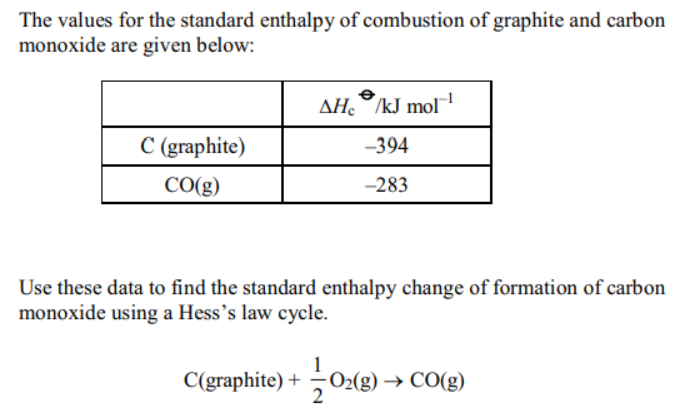
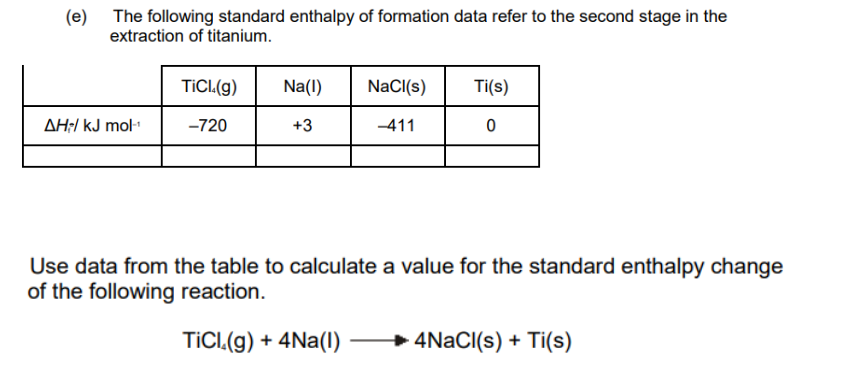
TRYING SOLVING THESE QUESTIONS
(DIFFICUILTY LEVEL – MODERATE TO HARD)
Video solution available
(Difficulty level – easy)
(Difficulty level – Easy to moderate)
Applications of Hess Cycle
Hess’s law plays a role in everyday life, from the meals people eat to the vehicles they use. It can be applied to calculate the energy content in food, which is listed as calories on nutrition labels. In reality, these calories represent kilocalories, where one kilocalorie equals 4184 joules.
This principle is also used to measure the energy content of fuels. Since different fuels vary in energy density, calculating the energy released during combustion helps companies identify which fuels are most efficient and cost-effective for their purposes.
Exam-Oriented Tips
- Always write the Hess’s cycle clearly.
- Label arrows with ΔH values in cycles.
- Double-check units (kJ mol⁻¹).
- Look for shortcuts — sometimes ΔH can be deduced quickly by combining two reactions.
- Practice multiple examples — examiners love Hess’s Law questions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Why is Hess’s Law important in chemistry?
Because it allows calculation of enthalpy changes for reactions that are difficult or impossible to measure directly.
Q2: Is Hess’s Law always true?
Yes, because it is based on the conservation of energy, which is a universal principle.
Q3: How is Hess’s Law applied in real life?
It’s used in fuels, materials, and chemical synthesis industries to calculate energy requirements.
Q4: What is the easiest way to remember Hess’s Law?
Think of it like taking different routes on a map — the distance between two points remains the same no matter which road you take.
Q5: Do I need to memorize all enthalpy values?
No, in exams enthalpy values are usually provided. What matters is knowing how to manipulate them correctly.
Learning Hess’s Law Effectively
Many students struggle with Hess’s Law because it involves cycles and indirect calculations. This is where personalized guidance helps. An experienced A level chemistry tutor can:
- Break down complex cycles step by step
- Provide past paper questions and solutions
- Teach shortcuts to save time in exams
- Build confidence through regular practice
If Hess’s Law feels tricky, working with a tutor ensures you don’t just memorize formulas but truly understand the logic behind them.
Additional Resource
For more visual explanations of enthalpy cycles and thermochemistry, you can explore this chemistry learning resource, which offers diagrams, solved problems, and revision tips.
Conclusion
Hess’s Law is one of the most powerful tools in thermochemistry. By proving that enthalpy change is independent of the pathway, it simplifies calculations, saves time, and supports practical chemistry in both academic and industrial contexts.
From combustion enthalpies to Born-Haber cycles, this principle is everywhere in A-Level Chemistry. For students, mastering Hess’s Law means fewer exam errors and a deeper understanding of energy conservation.
With practice — and perhaps with the help of an A level chemistry tutor — you can confidently solve even the toughest Hess’s Law questions.