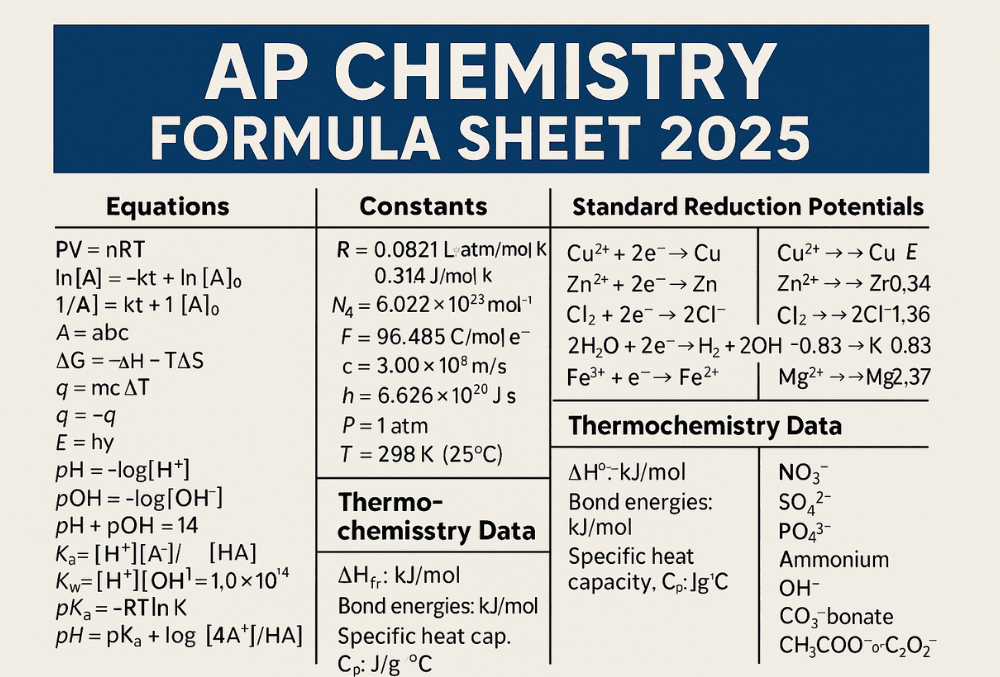
If you’re preparing for the AP Chemistry Exam in 2025, one of the most useful tools you’ll receive during the test is the official AP Chemistry Formula Sheet. This sheet, provided by the College Board, includes key equations, constants, and data to help you solve problems without memorizing everything.
In this blog, we’ll cover everything you need to know about the AP Chemistry Formula Sheet 2025: what it includes, what it doesn’t, and how to use it effectively.
What Is the AP Chemistry Formula Sheet?
The AP Chemistry Formula Sheet (officially called the “Equations and Constants Sheet”) is a two-page reference document provided to all students during the exam. You’ll receive it for both Section I (Multiple Choice) and Section II (Free Response).
It includes:
-
Key chemical equations
-
Constants and units
-
Data tables (e.g., standard reduction potentials)
-
Thermodynamic values
-
Common ions
Why Is It Important?
The formula sheet helps reduce the need to memorize complex equations. But it’s not enough to just have the formulas—you need to understand how and when to apply them. That’s why practicing with the sheet in advance is so important.
Full Breakdown of the AP Chemistry Formula Sheet 2025
Here’s a complete look at what’s included:
1. Common Equations
-
Ideal Gas Law: PV = nRT
-
First-Order Rate Law: ln[A] = -kt + ln[A₀]
-
Second-Order Rate Law: 1/[A] = kt + 1/[A₀]
-
Beer’s Law: A = abc
-
Gibbs Free Energy: ΔG = ΔH – TΔS
-
Electrochemical Free Energy: ΔG° = –nFE°
-
Heat Equation: q = mcΔT
-
Heat Exchange: q = –q
-
Energy of a Photon: E = hv
-
Speed of Light: c = λv
-
pH Equation: pH = –log[H⁺]
-
pOH Equation: pOH = –log[OH⁻]
-
Relationship: pH + pOH = 14
-
Acid Dissociation Constant: Ka = [H⁺][A⁻]/[HA]
-
Base Dissociation Constant: Kb = [OH⁻][HB⁺]/[B]
-
Water Constant: Kw = [H⁺][OH⁻] = 1.0 × 10⁻¹⁴
-
Equilibrium Constant: K = [products]ⁿ / [reactants]ⁿ
-
Free Energy & Equilibrium: ΔG° = –RT ln K
-
Nernst Equation: E = E° – (RT/nF) lnQ
-
pKa Formula: pKa = –log Ka
-
Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation: pH = pKa + log([A⁻]/[HA])
2. Constants and Units
-
Gas Constant (R):
-
0.0821 L·atm/mol·K
-
8.314 J/mol·K
-
-
Avogadro’s Number: 6.022 × 10²³ mol⁻¹
-
Speed of Light (c): 3.00 × 10⁸ m/s
-
Planck’s Constant (h): 6.626 × 10⁻³⁴ J·s
-
Faraday’s Constant (F): 96,485 C/mol·e⁻
-
Standard Temperature: 298 K
-
Standard Pressure: 1 atm
3. Thermochemistry and Electrochemistry
-
Enthalpy Change (ΔH)
-
Entropy Change (ΔS)
-
Free Energy Change (ΔG)
-
Heat Transfer: q = mcΔT
-
Standard Enthalpies of Formation (ΔH°f)
-
Gibbs Free Energy from Electrochemical Cells: ΔG° = –nFE°
-
Electrochemical cell potentials (E°) from half-reactions
4. Standard Reduction Potentials Table
This is a list of common half-reactions and their corresponding electrode potentials. Examples include:
-
Cu²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Cu E° = +0.34 V
-
Zn²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Zn E° = –0.76 V
-
Cl₂ + 2e⁻ → 2Cl⁻ E° = +1.36 V
This table is used to identify the anode, cathode, and spontaneity of redox reactions.
5. Bond Energies and Heat Capacities
Includes average bond enthalpies for common bonds (e.g., H-H, C-H, O-H) and specific heat of substances like water:
-
Specific Heat of Water = 4.18 J/g°C
6. Common Polyatomic Ions
A short list of polyatomic ions you’re expected to recognize, such as:
-
NO₃⁻ (Nitrate)
-
SO₄²⁻ (Sulfate)
-
CO₃²⁻ (Carbonate)
-
NH₄⁺ (Ammonium)
-
OH⁻ (Hydroxide)
-
PO₄³⁻ (Phosphate)
-
CH₃COO⁻ (Acetate)
What’s Not Included (But You Must Know)
The sheet doesn’t include everything, so here are formulas and concepts you’ll need to memorize:
-
Percent Composition = (mass of element / total mass) × 100%
-
Empirical and Molecular Formula Calculations
-
Formal Charge = Valence – (Bonds + Lone Electrons)
-
Molarity Formula: M = mol/L
-
M₁V₁ = M₂V₂ (dilutions)
-
VSEPR Geometry & Hybridization
-
Lewis Structures
-
Net Ionic Equations
-
Le Chatelier’s Principle
How to Use the Formula Sheet Effectively
-
Practice with it often: Use it while solving AP Chemistry practice questions.
-
Know where everything is: The more familiar you are with the layout, the faster you’ll find what you need during the exam.
-
Don’t rely on it alone: The sheet helps, but you must understand the context of each formula.
-
Simulate test conditions: Always practice using the sheet under timed conditions.
Final Thoughts
The AP Chemistry Formula Sheet 2025 is a must-know tool for exam day, but it’s only useful if you’ve practiced using it. Don’t wait until the exam to look at it—download it, study it, and solve questions with it regularly.
Understanding how to apply each formula will make you faster, more accurate, and more confident on test day.